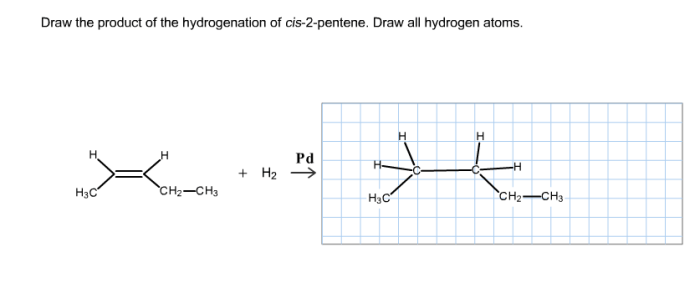
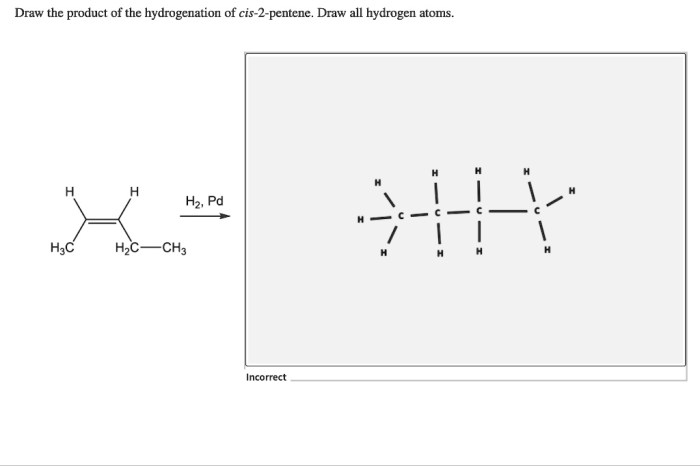
Draw the product of the hydrogenation of cis 2 pentene – In the realm of organic chemistry, hydrogenation stands as a transformative process, and when applied to cis-2-pentene, it unveils a fascinating journey of molecular metamorphosis. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of hydrogenation, guiding you through the mechanisms, stereochemistry, and practical applications of this remarkable reaction.
As we embark on this scientific expedition, we will dissect the step-by-step mechanism of hydrogenation, unraveling the role of catalysts and exploring the factors that influence the reaction’s outcome. Furthermore, we will delve into the physical and chemical properties of the hydrogenated product, uncovering its diverse applications in various industries.
Hydrogenation of cis-2-Pentene
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction that involves the addition of hydrogen to a compound, typically an unsaturated compound such as an alkene or alkyne. It is a widely used process in organic chemistry, particularly in the production of saturated hydrocarbons and other valuable chemicals.
Mechanism of Hydrogenation, Draw the product of the hydrogenation of cis 2 pentene
The hydrogenation of cis-2-pentene proceeds via a catalytic mechanism, typically using a metal catalyst such as palladium or platinum. The reaction involves the following steps:
- Adsorption of reactants:The cis-2-pentene and hydrogen molecules adsorb onto the surface of the catalyst.
- Formation of π-complex:The cis-2-pentene molecule forms a π-complex with the metal catalyst, where the double bond interacts with the metal center.
- Addition of hydrogen:Hydrogen molecules dissociate on the catalyst surface, and the hydrogen atoms add to the double bond of the π-complex, resulting in the formation of a metal-alkane complex.
- Desorption of product:The metal-alkane complex desorbs from the catalyst surface, releasing the product, pentane, into the reaction mixture.
The stereochemistry of the product is preserved during the hydrogenation reaction. The cis configuration of the double bond in cis-2-pentene is maintained in the product, pentane, because the hydrogen atoms add to the same side of the double bond.
Product of Hydrogenation
The product of the hydrogenation of cis-2-pentene is pentane, a saturated hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C5H12.
Pentane is a colorless, flammable liquid with a boiling point of 36.1 °C and a density of 0.626 g/mL. It is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as diethyl ether and petroleum ether.
Pentane is a relatively unreactive compound, but it can undergo combustion, halogenation, and nitration reactions. It is commonly used as a solvent, fuel, and starting material for the synthesis of other chemicals.
Factors Affecting Hydrogenation
The rate and selectivity of the hydrogenation reaction can be affected by several factors, including:
- Temperature:Higher temperatures generally increase the rate of hydrogenation.
- Pressure:Higher pressures increase the concentration of hydrogen in the reaction mixture, which can lead to faster hydrogenation.
- Catalyst activity:The activity of the catalyst is a crucial factor in determining the rate and selectivity of hydrogenation. Different catalysts have varying activities and selectivities, and the choice of catalyst depends on the specific reaction conditions and desired product.
Optimizing these factors is essential for achieving high product yield and purity in industrial hydrogenation processes.
Comparison with Other Alkenes
The hydrogenation of cis-2-pentene is similar to the hydrogenation of other alkenes, such as trans-2-pentene and 1-pentene.
The reaction mechanisms for the hydrogenation of these alkenes are analogous, involving the adsorption of reactants, formation of π-complexes, addition of hydrogen, and desorption of products. However, there are some differences in the stereochemistry of the products.
In the case of trans-2-pentene, the hydrogenation reaction also preserves the trans configuration, resulting in trans-pentane as the product. In contrast, the hydrogenation of 1-pentene produces a mixture of pentane isomers, including n-pentane and isopentane, due to the different orientations of the hydrogen atoms added to the double bond.
Q&A: Draw The Product Of The Hydrogenation Of Cis 2 Pentene
What is the significance of stereochemistry in the hydrogenation of cis-2-pentene?
Stereochemistry plays a crucial role in determining the orientation of the hydrogen atoms added during hydrogenation. In the case of cis-2-pentene, the cis configuration is preserved, resulting in the formation of a specific stereoisomer.
How does the catalyst influence the hydrogenation process?
Catalysts, such as palladium or platinum, facilitate the hydrogenation reaction by providing a surface for the reactants to adsorb and interact. They lower the activation energy of the reaction, making it more efficient and selective.
What are the industrial applications of hydrogenation?
Hydrogenation finds widespread use in industries such as petroleum refining, food processing, and pharmaceutical manufacturing. It is employed in processes like the production of margarine, the hydrogenation of vegetable oils, and the synthesis of various chemicals.